Calculating California sales tax
Learn how to calculate and apply California sales tax to stay compliant and avoid penalties for in-store & online sales.

Published on Monday 14th April 2025
Table of contents:
How much is sales tax in California?
California has a statewide tax rate of 7.25%, but the total tax can be higher depending on where you do business. Here’s how it works:
- 7.25% is the minimum tax rate statewide. It includes 6% for the state and 1.25% for local city and county funding.
- Some areas charge extra district taxes, between 0.1% to 2%, which can raise the total tax rate. Some areas may have more than one district tax in effect.
The total tax rate you charge is the sum of the statewide tax plus any local district tax. Your business must report and pay both local and state sales tax for all taxable sales and purchases.
California sales tax rate by county
The total tax you charge customers will depend on where your business operates. Counties and cities can add additional district taxes, causing rates to vary across the state, with some climbing over 10%.
Charging the correct sales tax ensures your business is in compliance with state regulations and can help you avoid costly penalties when you file your returns.
The table below provides a snapshot of how sales tax rates vary across different counties in California, based on additional district taxes:
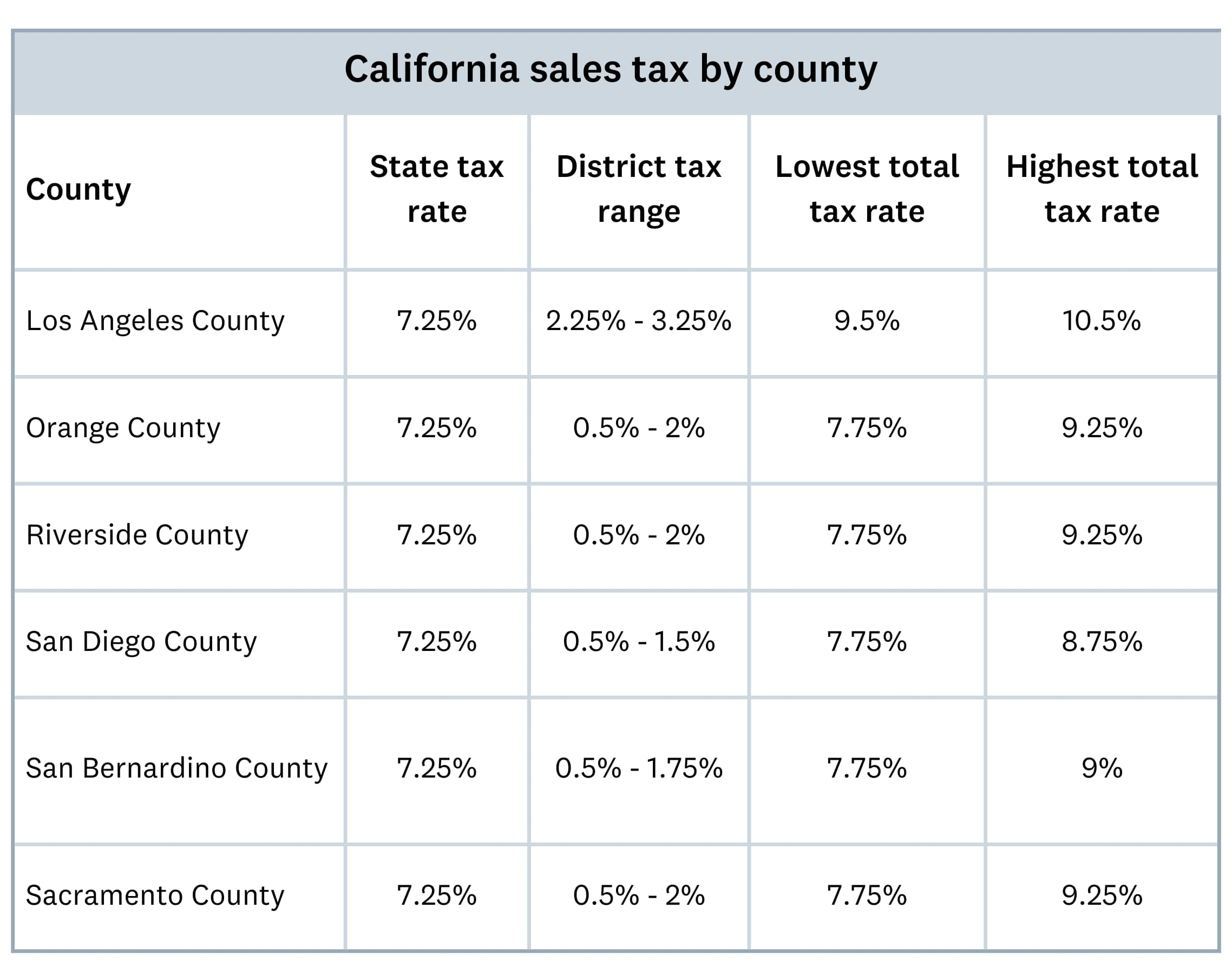
Let’s look at Los Angeles County as an example. Los Angeles County has a district tax of 2.25%, making the minimum total tax rate 9.5%. However some cities within the county might include additional city taxes, bringing the total higher than 9.5%.
The California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA) can give you an up-to-date breakdown of sales tax rates and fees by county and city. Use their official lookup tool to find the specific local rate for where you do business in the state.
How to calculate sales tax in California
If you are a first-time business owner, understanding how to calculate California sales tax can be overwhelming. Follow the steps below or use our sales tax calculator to help determine tax to charge.
Calculating tax starts with a simple formula: Sales tax = tax rate x item price.
Once you have the sales tax amount, simply add it to the product price to get the total cost you’ll charge the customer.
To calculate sales tax rates:
- Convert the tax rate to a decimal: Divide the tax rate by 100. For the California sales tax rate of 7.25%, this would be 7.25% / 100 = 0.0725.
- Calculate the tax amount: Multiply the item price by the tax rate. If an item costs $15.95, this would be 0.0725 (tax rate) x $15.95 (item price) = $1.15 in sales tax.
If you’re unsure of what the sales taxes are for your local jurisdiction, you can find the information you need on the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA) website. You can also use an online tool like Avalara’s sales tax calculator to determine tax rates.
Sales tax exemptions in California
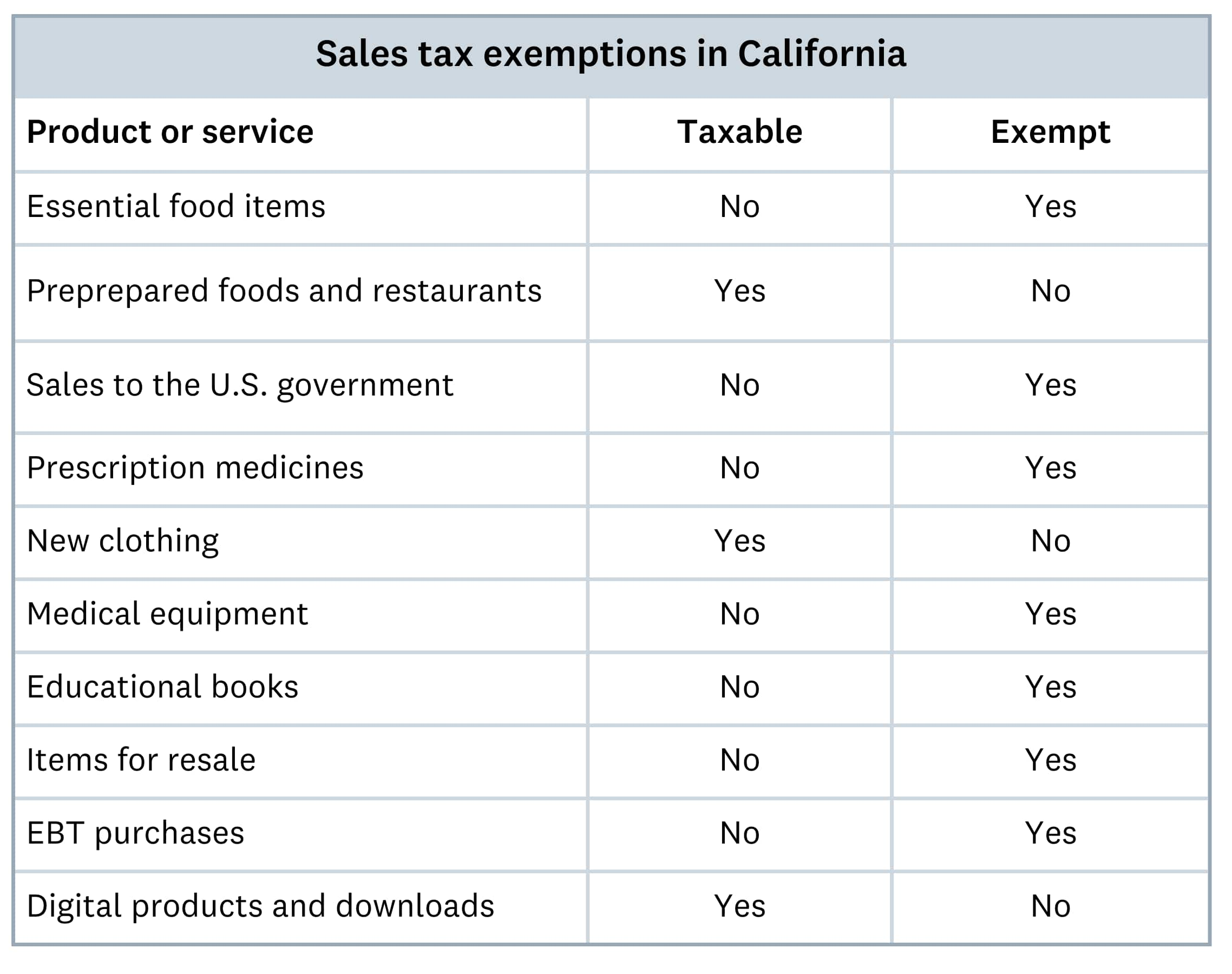
Retail sales of tangible products are generally subject to sales tax in California. These can include items like home goods, toys, digital products, and clothing. Some labor services are also subject to sales tax, especially if it involves producing new tangible goods.
Some items are classified as exempt, including certain food items, government services, and prescription medicines. A full list of nontaxable items can be found on the California Tax Service Center website.
Here’s a comparison between some taxable and non-taxable products in California:
Online sales tax rules for California businesses
If you sell products online, you might need to collect and pay California sales tax, even if your business isn’t physically located in the state. Under the California Wayfair Law (AB147), which took effect on April 1, 2019, businesses that sell products online must charge sales tax at the 7.25% state rate, plus any applicable local taxes if they meet certain criteria. Here’s what determines if your business needs to collect California sales tax:
- Physical presence: If your business has a physical location in California – like a store, warehouse, or office – you must collect sales tax on taxable sales made in the state. For example, a clothing boutique in San Francisco that also sells online to customers in other parts of California must charge sales tax for online purchases.
- Economic nexus: If your business has $500,000 or more in yearly sales to California customers, you must register and collect sales tax, even without a physical location in the state. For example, a Colorado based electronics retailer with $650,000 of online sales to California customers must collect sales tax on all shipments to California.
- Marketplace facilitators: Online platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy are required to collect and pay sales tax on behalf of sellers under California law.
Compliance steps for online sellers
If your business sells online to California residents, you must ensure compliance when collecting and paying sales tax. Follow these steps to stay compliant:
- Register for a California Seller’s permit. You must first register for a seller’s permit through the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA).
- Ensure you’re collecting the appropriate tax rate. Under California tax laws, your business must collect the correct tax rate for state, county, city, and district taxes (7.25% plus local district taxes). Use a California state tax calculator to apply the correct sales tax.
- File and pay sales tax regularly. Report and pay state taxes plus applicable local taxes based on your assigned filing frequency. For example, some businesses file quarterly while others can do so bi-annually or annually.
- Keep everything on record. Be sure to maintain detailed records of your business’s sales transactions for tax auditing purposes.
Use tax vs. sales tax in California
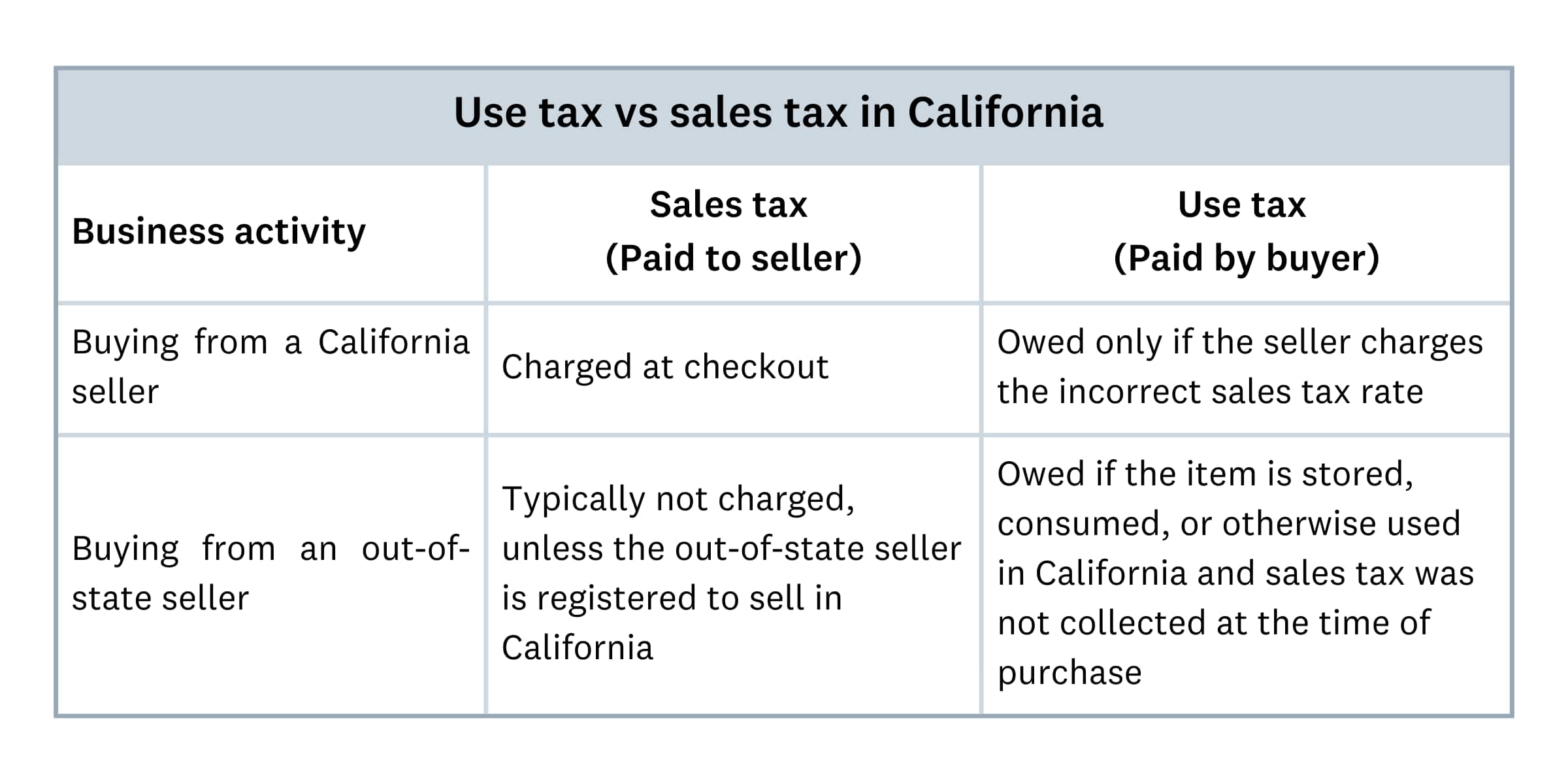
In California, both sales tax and use tax can apply to your business, depending on the transaction. Sales tax is collected by the seller at the time of purchase and goes to the CDTFA. However, buyers pay a use tax directly if sales tax is not collected at the time of purchase. Use tax will apply in different situations, so it’s vital to understand how it may apply to your business.
When does use tax apply?
Use tax may apply if:
- buying from an out-of-state seller who did not charge California sales tax, like ordering office supplies from a Nevada vendor who doesn’t collect California tax
- making an online transaction from a seller who does not collect California tax, such as equipment from a small online business
- making tax-free purchases that are later used in California, such as buying raw materials tax-free but using them in California
Here’s a breakdown of how use tax and sales tax work:
It can be helpful to use a California sales tax calculator to ensure your business is applying the correct rates for each transaction.
FAQs about California sales tax
Do businesses in California need a sales tax permit?
Yes, any business selling taxable goods or services in California must register for a seller’s permit with the CDTFA before collecting sales tax. The requirement to obtain the permit applies to all sole proprietors (individuals), corporations, partnerships, and limited liability companies (LLCs). Both retailers and wholesalers are also required to apply for a seller’s permit.
If you do not hold a seller’s permit and make sales temporarily (such as seasonal sales), you must apply for a temporary seller’s permit. The temporary permit applies to businesses and individuals where selling activities last no longer than 90 days at a single location.
How often do businesses need to file California sales tax returns?
Filing frequency depends on your sales volume. For instance, if you collect more than $1,000 per month in sales tax, you must file monthly. If your business collects between $601 and $1,000, filing is done quarterly. If the taxes your business collects amount to $600 or less in a year, then you will file annually.
What happens if a business doesn’t collect or remit sales tax in California?
Businesses that fail to collect or remit sales tax can face penalties, higher interest, and even legal action. The California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA) audits businesses and imposes fines, which can include a 10% penalty on unpaid sales tax plus the accrued interest.
Is labor subject to sales tax in California?
It depends on the type of labor. Physical labor that results in a tangible product, such as car repairs, furniture assembly, or appliance installation, is taxable. However, professional services like healthcare, consulting, or legal advice aren’t taxable. See the CDTFA website for more information on what type of labor is subject to sales tax.
Do nonprofit organizations have to pay California sales tax?
Yes. Most nonprofits have to pay sales tax unless they have a tax exempt status from the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA). Some of these exempt organizations include charitable organizations, cultural organizations like libraries and museums, veterans’ organizations, religious organizations, and educational organizations. If your business is a nonprofit, check with the CDTFA to ensure exemption status prior to selling.
Is there a sales tax on real estate transactions in California?
No, real estate sales aren’t subject to sales tax in California. However, a leased commercial property may be subject to California’s local district taxes depending on the leasing terms. For instance, a business leasing a warehouse to store products they sell online may be subject to local district taxes in their specific location.
Does California charge sales tax on vehicle purchases?
Yes. If you buy a car in California, the transaction is subject to the state’s base sales tax rate of 7.25%, plus any applicable local district taxes. If you purchase a vehicle from a private seller, you’ll need to self-report and pay the tax when you register the vehicle with the California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV).
How does California’s sales tax apply to shipping and delivery charges?
If shipping charges are separate from the item’s price, they’re not taxable. But if it’s bundled into the total price, or if the seller doesn’t allow you to arrange your own shipping, then the shipping charges are taxable. Read more on the CDTFA website.
Are digital goods and software subject to California sales tax?
Most digitally delivered goods like eBooks, online courses, and streaming services aren’t subject to sales tax. However, prepackaged software that you can download or keep on physical media is taxable.
Does California offer sales tax holidays?
No, California doesn’t have sales tax holidays. Unlike some states that temporarily exempt specific items for a designated time, California doesn’t do the same.
Start using Xero for free
Access Xero features for 30 days, then decide which plan best suits your business.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.