Calculating Texas sales tax
Learn how to calculate Texas sales tax, including local rates, to stay compliant when selling taxable goods or services

Published on Monday 7th April 2025
Table of contents:
How much is sales tax in Texas?
The Texas sales tax rate is 6.25%, but local jurisdictions can add their own district taxes, so the total tax depends on where you do business. Local tax rates can add up to 2%, making the maximum sales tax rate 8.25%. The total rate you charge is the sum of the statewide tax plus any local district tax.
Sales tax in Texas applies to retail sales, leases and rentals of most goods, and certain taxable services like cable television services and amusement services. However, some products are exempt from sales tax, which we cover in a later section.
Texas sales tax rates by location
Texas cities, counties, transit authorities, and special-purpose districts can impose additional local sales taxes. These local taxes are capped at 2%, meaning the maximum combined sales tax rate cannot exceed 8.25%. The exact rate your business collects depends on location. Local rates are important, especially if your business operates in more than one jurisdiction where tax requirements may differ.
Here’s an example of tax rates in several cities in Texas.
.1744351186849.png)
Since local business sales tax in Texas is updated periodically, it’s important to check the latest rates that apply to your business on the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts website.
How to calculate Texas sales tax
Sales tax can seem complicated, but it’s an important part of ensuring compliance with Texas’ state tax laws.
Use this simple formula to calculate Texas sales tax: Sales tax = tax rate x item price.
This formula gives you the amount in sales tax to add to the sale price to get the total cost to the customer.
To calculate Texas sales tax:
1. Convert the tax rate to a decimal: Divide by 100. For the Texas sales tax rate of 6.25%, this would be 6.25% / 100 = 0.0625.
2. Calculate the tax amount: Multiply the item price by the tax rate. For an item that costs $15.95, this would be 0.0625 (tax rate) x $15.95 (item price) = $0.996. Round the 3rd decimal to the nearest penny, making the tax $1.00.
If you’re unsure of what the sales taxes are for your local jurisdiction, you can find the information you need on the Texas sales tax page.
Check your local rates to ensure you apply the correct tax, or use an online tool like Avalara’s sales tax calculator.
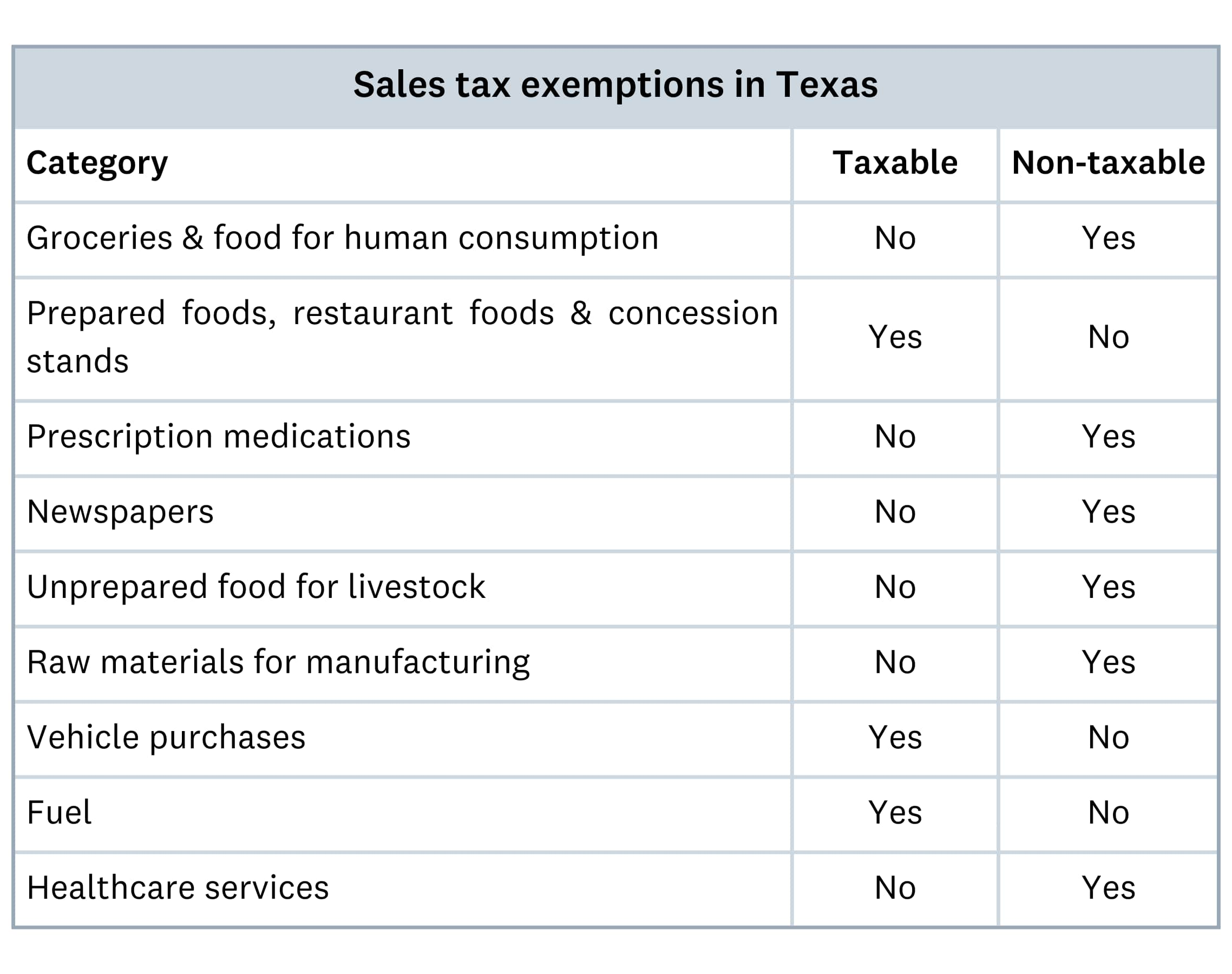
Sales tax exemptions in Texas
While sales tax applies to most retail goods, the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts has varying exceptions to taxable items. For example, products such as meat and produce food items, prescription medications, and certain medical devices are excluded from sales tax. Use the table below to understand some Texas tax exemptions:
Online sales tax rules for Texas businesses
If you sell products or services online, you may be required to collect sales tax in Texas, even if you don’t have a physical location in the state. According to the Texas Wayfair Law that went into effect on October 1, 2019, remote sellers and online marketplaces must collect and remit Texas sales tax (6.25%), plus any applicable local taxes, if they meet certain sales thresholds.
When are you required to collect Texas sales tax?
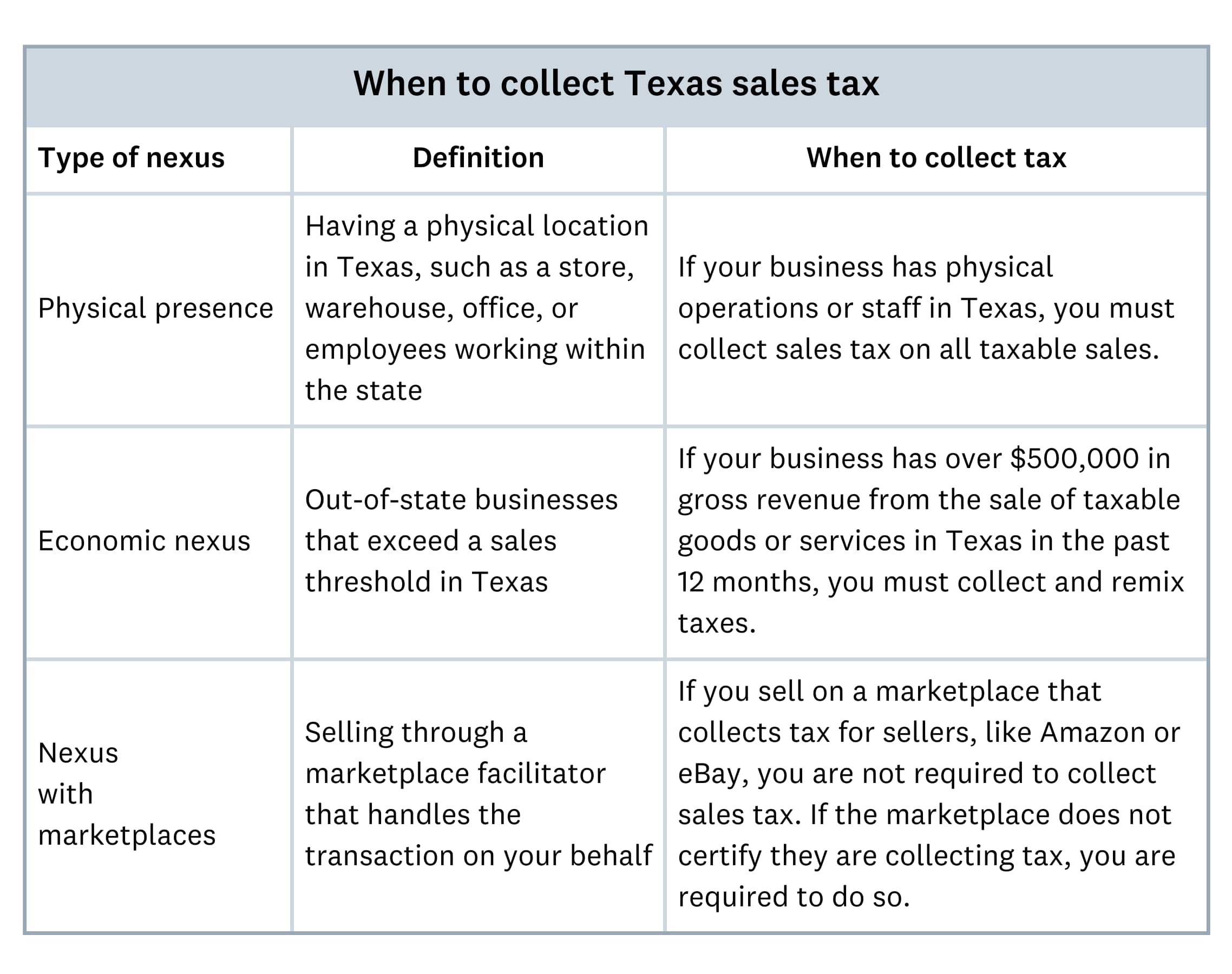
Follow these compliance steps for selling online.
1. Register for a Texas Sales and Use Tax Permit. You must register for a seller’s permit through the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts.
2. Ensure you’re collecting the correct tax. You must collect the appropriate tax rate, which includes the state rate of 6.25% plus any applicable local taxes.
3. File and remit sales tax regularly. File sales tax returns and pay the collected taxes based on the assigned filing frequency for your business. This could be quarterly, monthly, or yearly depending on your business.
4. Maintain business records. Keep detailed records of all transactions for at least four years, including sales through marketplaces.
Staying compliant with Texas online sales tax laws will help you avoid penalties and ensure proper tax collection.
Use tax vs. sales tax in Texas
Many businesses may also be subject to use taxes along with sales tax. While sales tax is collected by the seller at the time of purchase and is remitted to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts, use tax is a one-time tax that occurs when sales tax isn’t collected at the point of sale but the taxable good or service is stored, used or consumed in Texas.
Use tax applies to:
- out-of-state purchases where Texas sales tax isn’t collected
- online transactions from sellers who don’t collect sales tax
- tax-free purchases that are used in Texas
- purchases of taxable items in another country or state that are brought to Texas
For instance, if you purchase office equipment online from a seller that doesn’t charge sales tax, you must report and pay use tax directly to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts. Similarly, a Texas business that purchases manufacturing materials tax-free from an out-of-state vendor but uses the materials in Texas must pay use tax.
Below are some examples of how sales tax and use tax work:

FAQs about Texas sales tax
1. Do businesses in Texas need a sales tax permit?
Yes, any business selling taxable goods or services in Texas must register for a Texas Sales and Use Tax Permit with the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts before collecting sales tax. If your business has a physical presence, meets the economic nexus threshold of $500,000 in sales to Texas customers, or operates as a marketplace provider, you must apply for a sales tax permit.
2. How often do businesses need to file Texas sales tax returns?
Filing frequency in Texas depends on the amount of sales tax collected. The Texas Comptroller assigns a filing schedule – monthly, quarterly, or annually – when you apply for a sales tax permit.
3. Is labor subject to sales tax in Texas?
It depends on the type of labor. Labor that results in a taxable tangible product – such as furniture assembly, or appliance installation – is subject to sales tax in Texas. However, professional services like legal advice, medical services, and consulting are exempt. Certain repair and remodeling services for nonresidential property, such as hospitals, office buildings, or restaurants, may be subject to sales tax. For specific classifications, refer to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts.
4. Do nonprofit organizations have to pay Texas sales tax?
Most nonprofit organizations in Texas are required to pay sales tax unless they apply for and receive tax-exempt status from the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts. To qualify, organizations must meet specific criteria and obtain a Texas Sales and Use Tax Exemption Certificate. Certain purchases and sales by qualifying nonprofits may be exempt from sales tax, depending on the type of organization and activities.
5. Is there a sales tax on real estate transactions in Texas?
No, real estate sales are not subject to sales tax in Texas. However, certain commercial property leases may be subject to Texas sales and use tax, depending on the terms of the lease agreement. Additionally, real estate transactions may be subject to other taxes and fees, including property taxes and documentary transfer taxes.
6. Does Texas charge sales tax on vehicle purchases?
Yes, vehicles purchased in Texas are subject to the state's motor vehicle sales tax rate of 6.25%. This tax applies to purchases from dealerships and private sellers. If purchasing a vehicle from a private seller, the buyer must self-report and pay the tax when registering the vehicle with the Texas Department of Motor Vehicles (TxDMV). However, local sales taxes don’t apply to motor vehicle purchases.
7. How does Texas’s sales tax apply to shipping and delivery charges?
In Texas, shipping and delivery charges are generally taxable if the item being shipped is taxable. If a purchase is exempt from sales tax, the shipping charge is also exempt. If the seller includes shipping charges in the total price or does not allow the buyer to arrange their own shipping, the delivery charge is taxable. However, if shipping is separately stated and the item being shipped is not taxable, then the shipping charge is not subject to sales tax.
8. Are digital goods and software subject to Texas sales tax?
Yes, Texas imposes sales tax on many digital goods and software. Electronically transferred software, including prepackaged and custom software, is taxable, whether downloaded or accessed via the cloud. However, digital goods like eBooks, online courses, and streaming services are generally not taxable, unless they include taxable features such as downloadable software or additional services. Businesses should check with the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts for specific classifications.
9. Does Texas offer sales tax holidays?
Yes, Texas has several sales tax holidays throughout the year. During these designated periods, certain items are temporarily exempt from sales tax. Examples include:
- Back-to-School sales tax holiday (August): Exempts clothing, footwear, school supplies, and backpacks priced under $100.
- Energy Star sales tax holiday (May): Exempts qualifying Energy Star appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines.
- Emergency preparation sales tax holiday (April): Exempts emergency supplies like generators, batteries, and flashlights.
Be sure to refer to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts for exact dates and eligible items.
10. What happens if a business doesn’t collect or remit Texas sales tax?
Failure to collect or remit sales tax in Texas can result in penalties, interest, and legal action. The Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts may audit businesses and impose fines, including a 10% penalty on unpaid taxes, accrued interest on overdue amounts, and any additional penalties for repeated noncompliance, such as possible suspension of your business.
Disclaimer
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.
Start using Xero for free
Access Xero features for 30 days, then decide which plan best suits your business.